Safe Used Battery Collection
The Office of Environmental Health and Safety (OEHS) has over 40 battery recycling locations on campus. We supply properly labeled 5-gallon pails, which we collect annually for recycling. By taking a few extra steps when disposing of batteries in these pails, we can all play a role in reducing the potential risks to people, property, and the environment.
We are asking you to help “Avoid the Spark. Be Battery Safety Smart” and tape the exposed terminals of batteries, especially Lithium-ion batteries, before adding them to these pails.
Why do batteries need to be terminally protected?
Taping the exposed terminals of batteries (or alternatively, bagging) can help prevent the battery from rubbing against other batteries, metals, or potentially flammable materials, which could result in fires, personal injury or other damage. Use only clear tape (such as packing tape) for taping battery terminals, so waste disposal companies can clearly identify the type of battery. Alternatively, batteries can be placed in clear, sealable bags.
Which types of batteries do I need to protect?
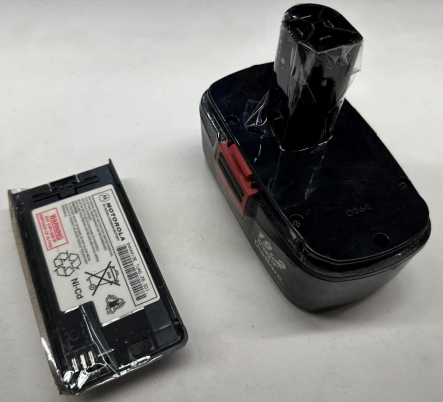
All rechargeable batteries need to be protected. This includes Nickel Cadmium (Ni-Cd, NiCad), Nickel Metal Hydride, Nickel Zinc, Lithium-Ion (Common Laptop), Small Sealed Lead Acid (Automobile), Lithium Coin Cell (Buttons). Additionally, any battery over 9 volts.
Lithium-based batteries pose a potential risk when not properly protected, as witnessed by several fires at recycling and waste facilities across the country. Lithium-based batteries should be collected separately from other types of batteries. If needed, request an additional pail from OEHS specifically for just lithium-based batteries (313-577-1200).
When in doubt, always tape or bag.
FOR MOST OF THESE BATTERIES, DO NOT TAPE BATTERIES TOGETHER OR COVER THE ENTIRE BATTERY WITH TAPE. ONLY THE TERMINALS! Coin cell batteries can be taped together on one strip of tape (as shown in the picture below), but the batteries should not be touching, especially the terminal sides.
Alkaline Batteries (Common Household) are the only batteries that do not require terminal taping.
ANY BATTERY THAT SHOWS EVIDENCE OF LEAKAGE, SPILLAGE OR DAMAGE MUST BE PLACED INSIDE A SEALABLE BAG.
List of current battery collection locations
Examples of common battery types and how to properly tape them:



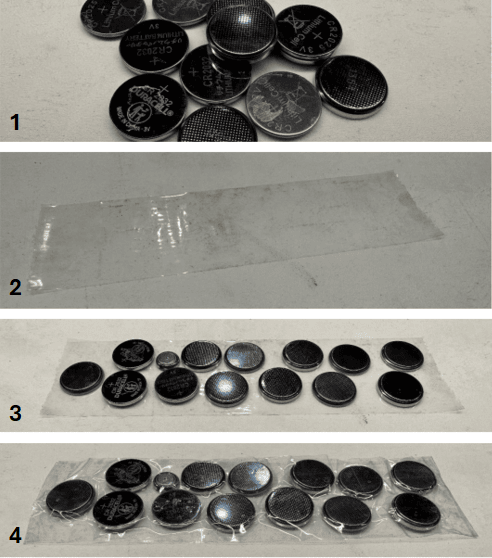
Source of pictures: First Choice Battery Guide
More information
To learn more about the hazards of used batteries and proper disposal, see the following resources.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Used Lithium-Ion Batteries.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Used Household Batteries.
- Call2Recycle, Inc. Avoid the Spark. Be Battery Safety Smart. Battery I.D. Guide.

This site may contain hypertext pointers to information created and maintained by other public and private organizations. Please be aware that we do not control or guarantee the accuracy, relevance, timeliness, or completeness of this outside information. Nor are they intended to endorse any views expressed or products or services offered by the author of the reference or the organization operating the site on which the reference is maintained.